Dentist-Recommended Treatments for Early-Stage Gum Disease
Understanding Early-Stage Gum Disease
Early-stage gum disease, commonly referred to as gingivitis, represents a crucial phase in the spectrum of gum health. It is characterized primarily by the inflammation of the gums, which is often a direct result of the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Understanding this condition involves recognizing both its causes and symptoms, as early intervention can prevent progression to more severe forms of periodontal disease.
The primary cause of early-stage gum disease is plaque buildup. When dental hygiene practices are inadequate, plaque can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by professional dental cleaning. This buildup leads to a cycle of inflammation, where the body’s immune response reacts to the bacteria in plaque, resulting in swollen, red gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. Several factors can exacerbate the development of gingivitis, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes (such as those occurring during pregnancy or menopause), certain medical conditions (like diabetes), and nutritional deficiencies.
Symptoms of early-stage gum disease often present subtly, which can lead individuals to underestimate the severity of their condition. Initial signs may include persistent bad breath, swollen or tender gums, and a change in gum color from a healthy pink to a red hue. Some patients may also notice that their gums bleed during daily oral hygiene practices. Recognizing these early indicators is essential, as timely intervention can reverse the condition and restore gum health. Regular dental check-ups ensure that any signs of gingivitis are addressed promptly, minimizing the risk for more severe gum diseases in the future.
Importance of Professional Dental Assessments
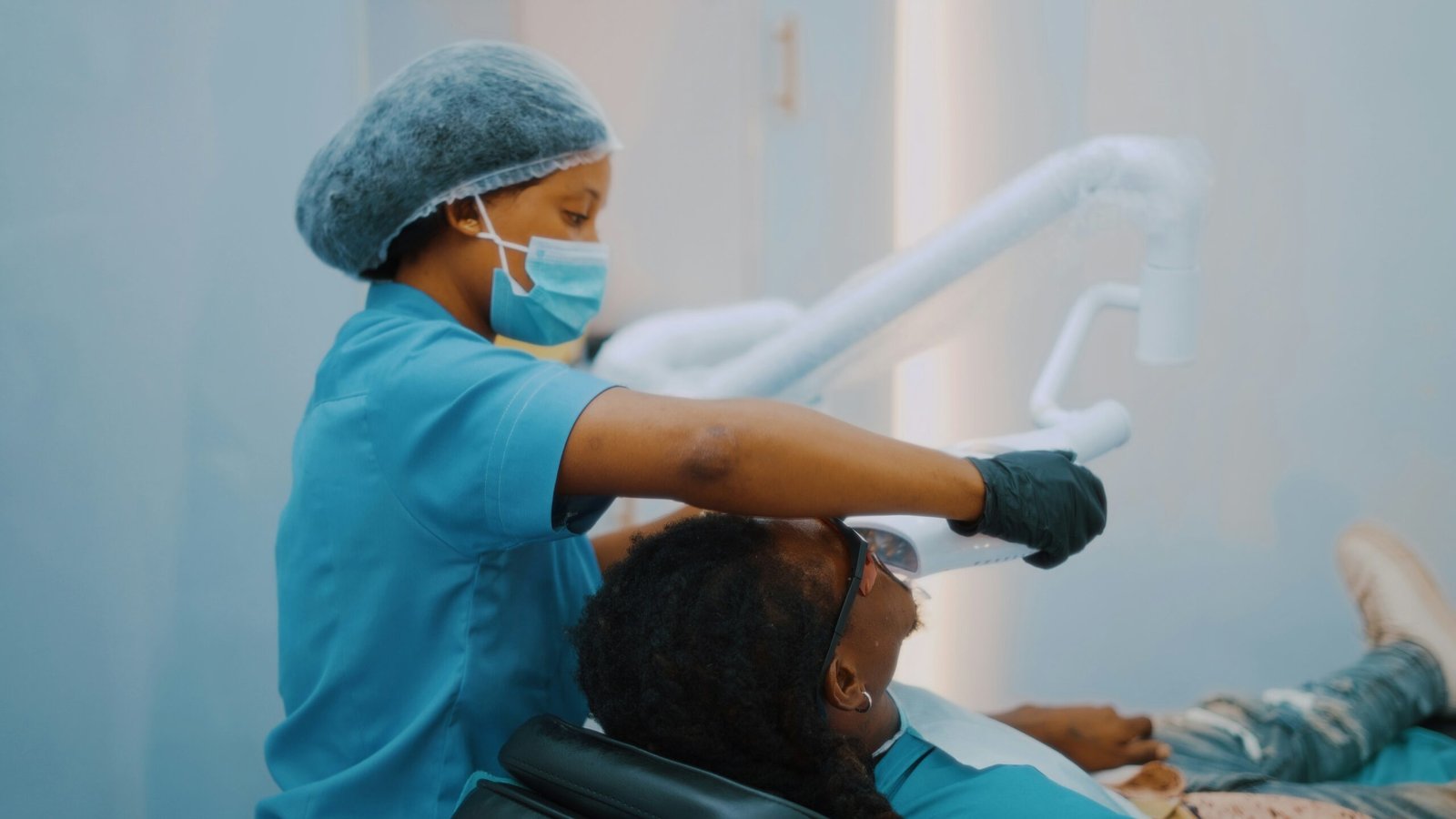
Regular dental check-ups play a fundamental role in identifying and managing early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. These appointments allow dental professionals to assess an individual’s gum health systematically. During a typical dental evaluation, the clinician examines the gums using various tools and techniques to determine if any signs of inflammation or infection are present.
One of the primary tools used during a dental assessment is the periodontal probe, a calibrated instrument that measures the depth of the gum pockets around each tooth. Healthy gums typically present with pocket depths of 1-3 millimeters, whereas increased measurements can indicate gum disease. Dentists may also visually inspect the gum tissue for swelling, redness, or bleeding, which are identifiable symptoms of gum disease.
In addition to physical examination, dentists often utilize digital imaging technologies, such as X-rays, to evaluate the underlying structures of the teeth and jaw. These imaging tools help in identifying any bone loss that may be associated with advanced gum disease, allowing for timely intervention. Early detection through such comprehensive assessments is crucial, as untreated gum disease can lead to more severe conditions, like periodontitis, which can result in tooth loss and other systemic health issues.
Regular dental assessments not only serve to identify potential issues early on but also provide an opportunity for dental professionals to educate patients about proper oral hygiene practices. Dentists can offer personalized advice tailored to individual needs, reinforcing the importance of maintaining optimal gum health at home. Consequently, by prioritizing regular dental check-ups, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of progressing from early-stage gum disease to more advanced stages requiring intensive treatment.
Effective Home Care Practices
Maintaining optimal oral hygiene is essential in managing early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. This condition can often be reversed with proper dental care practices at home. The primary focus should be on effective brushing techniques, regular flossing, and the use of therapeutic mouth rinses, all of which contribute significantly to overall gum health.
Brushing the teeth effectively is the cornerstone of personal dental hygiene. It is important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Dentists recommend brushing at least twice a day for a duration of two minutes each time. To ensure thorough cleaning, the brush should be held at a 45-degree angle to the gums, employing gentle circular motions. This technique is not only effective in removing plaque from the teeth but also aids in cleansing the gum line, where bacteria tend to accumulate.
Equally vital is the practice of regular flossing. Flossing helps to remove food particles and plaque that may be trapped between the teeth and beneath the gum line, where a toothbrush cannot reach. It is advisable to floss at least once a day, and individuals should ensure they are using the correct technique by gently sliding the floss against the sides of each tooth and beneath the gum line, avoiding any snapping action that could injure the gums.
The incorporation of an antimicrobial or therapeutic mouth rinse can also prove beneficial for those battling early-stage gum disease. These rinses can reduce plaque buildup and improve gum health. Regular use not only provides additional cleansing but also offers a more comprehensive approach to oral hygiene.
Consistency is key. Establishing and adhering to a daily routine of brushing, flossing, and rinsing will significantly increase the chances of managing and reversing early-stage gum disease. Through these effective home care practices, individuals can enhance their oral health and maintain healthier gums.
Scaling and Root Planing: The First Line Treatment
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical periodontal treatment that serves as the first line of defense against early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. This procedure is designed to remove plaque and tartar buildup from the surfaces of the teeth and the roots, which, if left untreated, can lead to more severe forms of gum disease.
The treatment begins with a thorough examination of the gums and teeth by a dental professional, who assesses the extent of gum disease. Using specialized instruments, the dentist or hygienist then performs scaling, which involves scraping away plaque, tartar, and bacteria from both above and below the gum line. Following this, root planing is conducted to smooth out the tooth root surfaces, making it more difficult for bacteria to adhere and re-establish themselves. This two-step approach helps in re-establishing a healthy environment for the gums, promoting healing and reattachment of gum tissue to the teeth.
One of the primary benefits of scaling and root planing is its effectiveness in reversing early-stage gum disease. By thoroughly cleaning the tooth surfaces, it removes harmful bacteria while reducing inflammation of the gums. Patients often experience noticeable improvements in gum health within a short period following the treatment. Additionally, with proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental visits, the risk of progressing to more advanced stages of gum disease can be significantly mitigated.
The expected outcomes of scaling and root planing largely depend on the patient’s commitment to maintaining good dental hygiene post-treatment. Many individuals see a reduction in gum bleeding, swelling, and discomfort, enhancing overall oral health. In conclusion, scaling and root planing is a critical process for managing early-stage gum disease and is highly recommended by dental professionals for its proven efficacy.
Antimicrobial Treatments and Medications
Antimicrobial treatments play a crucial role in addressing early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. These therapies aim to reduce bacterial presence in the oral cavity, ultimately leading to improved gum health. Dentists often prescribe various forms of antibacterial medication to assist their patients in managing this condition effectively.
One of the most common types of antimicrobial treatments is antibacterial mouthwashes. These mouth rinses often contain chlorhexidine or essential oils that help to reduce plaque accumulation and combat bacteria that contribute to gum disease. Chlorhexidine mouthwashes are particularly effective for short-term use, especially following dental procedures. They work by penetrating the bacterial cell walls, thus diminishing bacterial growth and helping to restore gum health.
In addition to mouthwashes, dentists may recommend topical antibiotics. These medications are delivered directly to the affected areas of the gums, allowing for targeted treatment. Common topical antibiotics include minocycline and doxycycline, which are inserted into the gum pockets. These treatments help to reduce inflammation and eradicate bacterial infections that cause gum issues.
Systemic medications, such as oral antibiotics, may also be prescribed by dentists to treat more extensive gum disease. These medications enter the bloodstream and can help address infections that are not confined to localized areas. Drugs like amoxicillin are often used in combination with other treatments to provide comprehensive care for patients suffering from early-stage gum disease.
Overall, the utilization of antimicrobial treatments and medications by dentists is essential for managing and reversing early-stage gum disease. By effectively reducing bacterial presence and supporting gum health, these interventions can lead to significant improvements in oral hygiene and patient outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes That Support Gum Health
Maintaining optimal gum health is essential in preventing and managing early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. One of the most significant lifestyle changes that individuals can adopt is smoking cessation. Studies consistently show that tobacco use contributes to gum disease progression by impairing blood flow to the gums and inhibiting healing. Quitting smoking not only improves oral health but also enhances overall wellbeing, reducing the risk of various chronic diseases.
Dietary adjustments play a vital role in enhancing oral health as well. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can strengthen gum tissue. Foods high in vitamin C, such as oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers, are particularly beneficial in preventing gum inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and can also have a positive effect on gum health. Conversely, reducing intake of sugary foods and beverages is crucial, as sugar contributes to plaque formation, a primary cause of gum disease.
Furthermore, managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, is essential for maintaining healthy gums. Research indicates that individuals with uncontrolled diabetes are at an increased risk for gum disease due to elevated blood sugar levels that can lead to bacterial growth. Regular monitoring and effective management of blood glucose can significantly impact oral health. Those with diabetes should maintain consistent communication with their healthcare providers, including dental professionals, to ensure a comprehensive care approach.
In summary, embracing lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes can significantly support gum health. Such transformations not only contribute to the treatment of early-stage gum disease but also foster a long-term commitment to overall oral hygiene.
The Role of Regular Follow-Ups
Regular follow-up appointments play a crucial role in the effective management of early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis. After the initial treatment, which often includes professional cleaning and education about proper oral hygiene techniques, these subsequent visits serve multiple essential purposes. One of the primary aims of regular follow-ups is to monitor the progress of gum health. During each appointment, your dentist will assess the condition of your gums and determine if the initial treatment has effectively reduced inflammation and improved overall oral health.
In addition to progress monitoring, these follow-up visits offer an opportunity for dental professionals to adapt treatment plans as necessary. As each individual responds differently to initial interventions, it may be necessary to modify the approach based on observed outcomes. For instance, additional cleanings or more advanced therapies might be recommended if there is little to no improvement or if the condition worsens. This adaptability is vital for ensuring a tailored treatment that meets the specific needs of the patient, thereby enhancing the likelihood of recovery from early-stage gum disease.
Furthermore, regular follow-ups reinforce the importance of good dental hygiene practices. During these visits, dental professionals can provide ongoing education about effective brushing and flossing techniques tailored for gum health. This training is essential, as strong home care routines significantly contribute to long-term success in maintaining healthy gums. By establishing a consistent schedule of follow-up appointments, patients are more likely to stay motivated and committed to their oral care, which is pivotal in preventing the progression of gum disease.
Recognizing the Signs of Progression
Early-stage gum disease, commonly known as gingivitis, often presents with subtle signs that can easily be overlooked. Recognizing these signs is crucial as they mark the transition from a manageable condition to a more severe form of gum disease, potentially leading to periodontitis. One of the primary symptoms to watch for is persistent redness and swelling of the gums. Healthy gums should appear firm and pale pink, while inflamed gums are often swollen and may look shiny. This is often accompanied by bleeding during brushing or flossing, which can indicate a worsening condition.
Another symptom is persistent bad breath, medically referred to as halitosis. This unpleasant odor can be due to the buildup of plaque and bacteria along the gum line, suggesting that the current gum health may be deteriorating. Furthermore, individuals may experience increased sensitivity in their teeth, particularly when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. This heightened sensitivity can signal the presence of deeper underlying problems that require professional attention.
As gum disease progresses, patients may also notice pockets forming between the teeth and gums, which can trap food particles and bacteria. This not only exacerbates the condition but makes it harder to maintain proper oral hygiene. Tooth mobility or changes in the alignment of teeth are further signs of an advancing gum disease, indicating that immediate intervention is necessary.
Addressing these symptoms with a dental professional as soon as they arise is vital for effective management of gum disease. Ignoring the signs can lead to irreversible damage, affecting not just oral health but overall well-being. Regular dental check-ups and vigilant self-care are essential to prevent the progression of early-stage gum disease into more severe forms.
Conclusion: Taking Charge of Your Gum Health
In conclusion, maintaining gum health is paramount in preventing advanced stages of gum disease, which can lead to complications such as tooth loss and systemic health issues. The strategies discussed in this blog post encompass professional dental treatments and recommended at-home care routines that can significantly affect gum health outcomes. It is crucial to recognize the signs of early-stage gum disease, such as redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing. Timely intervention can halt the progression of the disease and restore healthy gums.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are vital components of proactive oral care, allowing dental professionals to identify and address gum disease at its initial stages. Moreover, adopting good oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing, serve as the first line of defense against gum disease. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in nutrients can also support gum health and overall wellness.
Engaging with your dentist about any concerns, including changes in your oral health, is essential. Your dental care provider can offer tailored advice and recommend treatments appropriate for your specific needs. By taking charge of your gum health, you not only enhance your oral hygiene but also contribute positively to your general health.
Ultimately, gum disease is manageable with awareness and attentiveness. Remember, early detection and intervention are critical to preventing serious consequences. It’s imperative to stay informed and proactive about your dental care to ensure your gums remain healthy and strong. The commitment to maintaining your gum health today will pay off in the long-run, leading to a healthy smile and improved quality of life.